A CTF organized by a team from Malaysia. It was a tidy little event with some interesting challenges.
Crypto
N-less RSA
This is a RSA challenge with unknown N, but we have the totient function phi(n). We are also provided the logic used to determine the private primes p and q.
def generate_secure_primes():
p = getStrongPrime(1024)
q = int(next_prime(p*13-37*0xcafebabe))
return p,q
# Generate two large and secure prime numbers
p,q = generate_secure_primes()
n = p*q
e = 0x10001
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
c = pow(bytes_to_long(flag),e,n)
# we are given phi, e and c, but not n
Given that we have phi and the relationship between p and q, we can solve for them using any of the following three methods.
Method 1: By factoring phi
# Use https://www.alpertron.com.ar/ECM.HTM to factor phi
from Crypto.Util.number import isPrime, long_to_bytes
from itertools import combinations
from functools import reduce
phi=340577739943302989719266782993735388309601832841016828686908999285012058530245805484748627329704139660173847425945160209180457321640204169512394827638011632306948785371994403007162635069343890640834477848338513291328321869076466503121338131643337897699133626182018407919166459719722436289514139437666592605970785141028842985108396221727683676279586155612945405799488550847950427003696307451671161762595060053112199628695991211895821814191763549926078643283870094478487353620765318396817109504580775042655552744298269080426470735712833027091210437312338074255871034468366218998780550658136080613292844182216509397934480
e=65537
ct=42363396533514892337794168740335890147978814270714150292304680028514711494019233652215720372759517148247019429253856607405178460072049996513931921948067945946086278782910016494966199807084840772350780861440737097778578207929043800432279437709296060384506082883401105820800844187947410153745248466533960754243807208804084908637481187348394987532434982032302570226378255458486161579167482667571132674473067323283939026297508548130085016660893371076973067425309491443342096329853486075971866389182944671697660246503465740169215121081002338163263904954365965203570590704089906222868145676419033148652705335290006075758484
factors = [2,2,2,2,5,17,23,127,34883,64327,31855469,41906999093,103832676376161046043,
42928682841447187075836289855892629156535900514107927517684293084786844441409957297894592527460787241683614840492974772427636887719994128565592152980944126724469079274172144474672062412412603584793646346956898729686409791648474545298852872995161295471414165954724402947,
6420760786362823769296653774296236632402429318675915367452603711386456193709958608737754568883471330653872083531628632121784399208909036073963921230370375260817560046504060944356316155772191086712627421688528565251967757404295337261653707746185260317688974197060087034705221140112831521071507609
]
print(len(factors))
# Work out which combination (product) of factors produce possible values for P-1 and Q-1
for n in range(1, len(factors)):
comb = combinations(factors, n)
print(f"testing [C({n})]...")
for c in comb:
prod = reduce(int.__mul__, c)
# find the product of all the factors and see if it is 1 less than a prime number
if isPrime(prod+1) and isPrime(phi//prod+1):
p = prod+1
q = phi//(p-1) + 1
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
pt = pow(ct, d, p*q)
m = long_to_bytes(pt)
# print(m.decode())
if b"wgmy" in m:
exit(m.decode())
Method 2: Bruteforce + quadratic roots to determine p
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
F.<p> = ZZ[]
# given
phi=340577739943302989719266782993735388309601832841016828686908999285012058530245805484748627329704139660173847425945160209180457321640204169512394827638011632306948785371994403007162635069343890640834477848338513291328321869076466503121338131643337897699133626182018407919166459719722436289514139437666592605970785141028842985108396221727683676279586155612945405799488550847950427003696307451671161762595060053112199628695991211895821814191763549926078643283870094478487353620765318396817109504580775042655552744298269080426470735712833027091210437312338074255871034468366218998780550658136080613292844182216509397934480
e=65537
c=42363396533514892337794168740335890147978814270714150292304680028514711494019233652215720372759517148247019429253856607405178460072049996513931921948067945946086278782910016494966199807084840772350780861440737097778578207929043800432279437709296060384506082883401105820800844187947410153745248466533960754243807208804084908637481187348394987532434982032302570226378255458486161579167482667571132674473067323283939026297508548130085016660893371076973067425309491443342096329853486075971866389182944671697660246503465740169215121081002338163263904954365965203570590704089906222868145676419033148652705335290006075758484
for i in range(1000):
f = (p - 1) * (p*13-37*0xcafebabe + i) - phi
if (len(f.roots()) != 0):
p = f.roots()[0][0]
q = phi // (p - 1) + 1
assert phi % (p - 1) == 0
assert phi % (q - 1) == 0
n = p * q
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
m = pow(c, d, n)
print(long_to_bytes(m))
break
Method 3: Z3 solver
from z3 import *
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
# given
phi=340577739943302989719266782993735388309601832841016828686908999285012058530245805484748627329704139660173847425945160209180457321640204169512394827638011632306948785371994403007162635069343890640834477848338513291328321869076466503121338131643337897699133626182018407919166459719722436289514139437666592605970785141028842985108396221727683676279586155612945405799488550847950427003696307451671161762595060053112199628695991211895821814191763549926078643283870094478487353620765318396817109504580775042655552744298269080426470735712833027091210437312338074255871034468366218998780550658136080613292844182216509397934480
e=65537
c=42363396533514892337794168740335890147978814270714150292304680028514711494019233652215720372759517148247019429253856607405178460072049996513931921948067945946086278782910016494966199807084840772350780861440737097778578207929043800432279437709296060384506082883401105820800844187947410153745248466533960754243807208804084908637481187348394987532434982032302570226378255458486161579167482667571132674473067323283939026297508548130085016660893371076973067425309491443342096329853486075971866389182944671697660246503465740169215121081002338163263904954365965203570590704089906222868145676419033148652705335290006075758484
p = Int('p')
q = Int('q')
incr = Int('incr')
s = Solver()
s.add((p-1) * (q-1) == phi)
s.add(q == (p*13-37*0xcafebabe + incr))
# set the boundary conditions p, q and incr all should be positive integers
s.add(p > 0)
s.add(q > 0)
s.add(incr > 0)
# set an upper bound to `incr` as the nextPrime() should find one close to the start value (13p - k)
s.add(incr < 1000) # tune as needed.
if s.check() == sat:
m = s.model()
P = m[p].as_long()
Q = m[q].as_long()
N = P*Q
print(f'Found Solution: \n{P =}\n{Q =}')
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(c, d, N))) # b'wgmy{a9722440198c2abad490478875be2815}'
else:
print('Unsat :(')
Method 4:
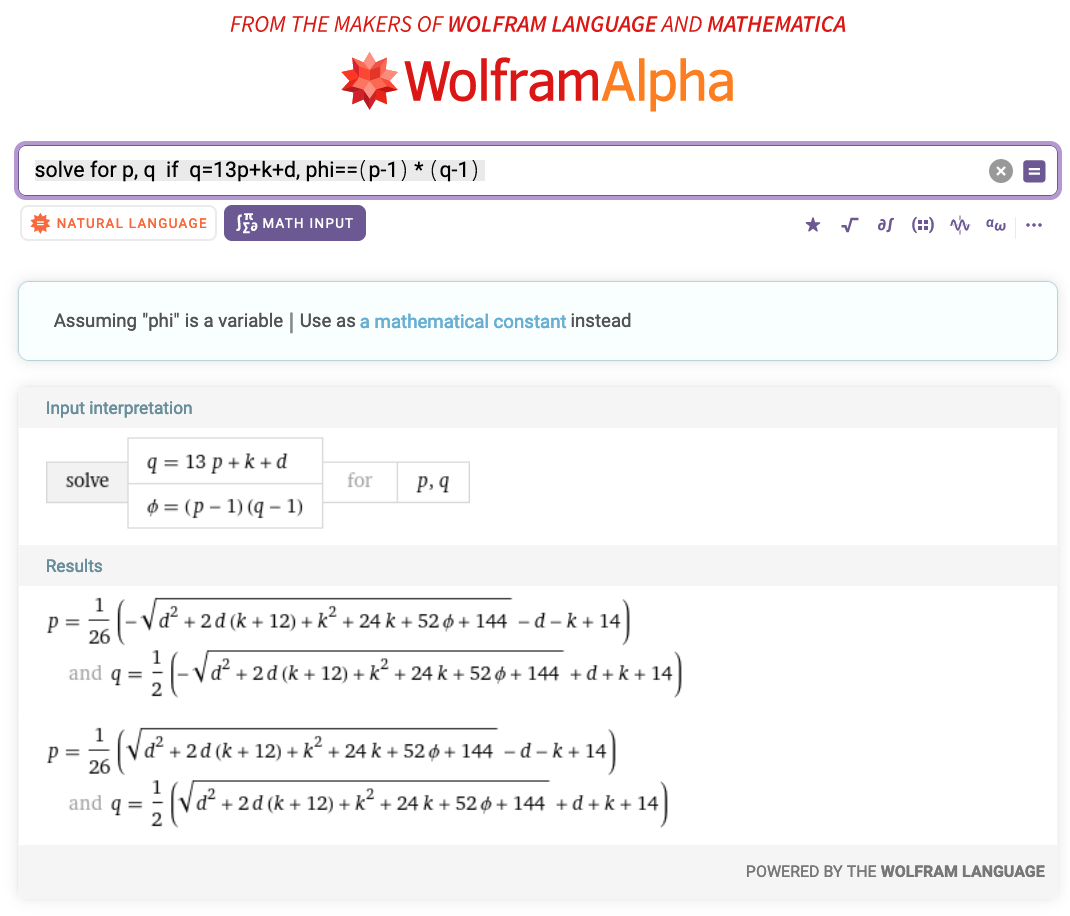
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
# given
phi=340577739943302989719266782993735388309601832841016828686908999285012058530245805484748627329704139660173847425945160209180457321640204169512394827638011632306948785371994403007162635069343890640834477848338513291328321869076466503121338131643337897699133626182018407919166459719722436289514139437666592605970785141028842985108396221727683676279586155612945405799488550847950427003696307451671161762595060053112199628695991211895821814191763549926078643283870094478487353620765318396817109504580775042655552744298269080426470735712833027091210437312338074255871034468366218998780550658136080613292844182216509397934480
e=65537
c=42363396533514892337794168740335890147978814270714150292304680028514711494019233652215720372759517148247019429253856607405178460072049996513931921948067945946086278782910016494966199807084840772350780861440737097778578207929043800432279437709296060384506082883401105820800844187947410153745248466533960754243807208804084908637481187348394987532434982032302570226378255458486161579167482667571132674473067323283939026297508548130085016660893371076973067425309491443342096329853486075971866389182944671697660246503465740169215121081002338163263904954365965203570590704089906222868145676419033148652705335290006075758484
k = -37*0xcafebabe
d = 0
while True:
q = ( sqrt(d^2 + 2*d*(k+12) + k^2 + 24*k + 52*phi + 144) +d +k +14)/2
if q in ZZ:
break
d += 1
p = (phi/(q-1)) +1
n = p*q
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(c,d,n)))
Ho Ho Ho 2
Want to make a wish for this Christmas? Submit here and we will tell Santa!!
1. Register
2. Login
3. Make a wish
4. Wishlist (Santa Only)
5. Exit
Enter option: 1
Enter your name: aaaaaa
Use this token to login: 6076a84d0f90efbfb4a2ddc7a3f1436f
To solve this challenge, we need to login with the name with Santa Claus in it and have a valid token.
The token generator is a LCG with just one randomly generated value
m = 0xb00ce3d162f598b408e9a0f64b815b2f
a = 0xaaa87c7c30adc1dcd06573702b126d0d
c = 0xcaacf9ebce1cdf5649126bc06e69a5bb
n = getRandomNBitInteger(64)
def generateToken(name):
x = bytes_to_long(name.encode(errors="surrogateescape"))
# LCG fast skip implementation
# is equivalent to the following code
# for _ in range(n):
# x = (a*x + c) % m
x = ((pow(a, n, (a-1)*m) - 1) // (a-1) * c + pow(a, n, m) * x) % m
return hex(x)[2:]
The algorithm for the fast skip LCG calculation is explained very well at this site.
$$ Token \quad T = \overbrace{[[x\cdot a + c]\cdot a + c] \cdots + c]]}^{\text{nested n-times}}\\ T = x\cdot a^n + c\cdot a^{n-1}+ c\cdot a^{n-2}+ \cdots + c \\ T = x\cdot a^n + c\cdot ( a^{n-1} + a^{n-2} + \cdots + 1 ) \\ T = x\cdot a^n + c\cdot (\dfrac{a^n-1}{a-1}) \pmod{m}\\ \space \\ \text {Given x, m, a, c and T, calculate n}\\ \space \\ T \cdot {(a-1)} = x\cdot{a^n}\cdot{(a-1)} + c\cdot{a^n} - c\\ T \cdot {(a-1)}+c = x\cdot{(a-1)}\cdot{a^n} + c\cdot{a^n}\\ T\cdot{(a-1)}+c = {a^n}\cdot{(x\cdot{(a-1)} + c)} \\ {a^n} = \dfrac{ T\cdot{(a-1)}+c}{x\cdot{(a-1)} + c}\\ \space \\ {n} = {log_a} \Big[ \dfrac{ T\cdot{(a-1)}+c}{x\cdot{(a-1)} + c} \Big] \pmod {m} \space \\ \space \\ \text {In Sage, use the following equation and simplify to solve for } a^n \\ T = x\cdot a^n + c\cdot (\dfrac{a^n-1}{a-1}) \pmod{m}\\ x\cdot a^n + c\cdot (\dfrac{a^n-1}{a-1}) - T =0 \pmod{m}\\ $$
The full solution is:
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long
def regUser(R, username):
R.recvuntil(b'Enter option:')
R.sendline(b'1')
R.recvuntil(b'name:')
R.sendline(username)
R.recvuntil(b'to login:')
t = R.recvline().strip()
return t
R = process(['python3', 'hohoho1-server.py'])
# R = remote('',)
context.log_level = 'debug'
uname = b'aaaaaaaa'
t = regUser(R, uname)
print(f"{uname} --> {t}")
m = 0xb00ce3d162f598b408e9a0f64b815b2f
a = 0xaaa87c7c30adc1dcd06573702b126d0d
c = 0xcaacf9ebce1cdf5649126bc06e69a5bb
T = int(t, 16)
x = bytes_to_long(uname)
# `p` is the variable to represent a**n
# T = a^n x + c (a^n - 1)/(a-1)
# a^n (is not xor)
F.<p> = Zmod(m)[]
f = p*x + c * (p - 1) / (a - 1) - T
print(f"Simplified equation: {f = } = 0")
lst = f.coefficients()
an = (-lst[0]) / lst[1]
print(f"Coeff {lst = }\n {an = }")
# Find discrete log with base `a` to get `n`
n = int(an.log(a))
print(f"Found {n = }")
def generateToken(name):
x = bytes_to_long(name.encode(errors="surrogateescape"))
x = ((pow(a, n, (a-1)*m) - 1) // (a-1) * c + pow(a, n, m) * x) % m
return hex(x)[2:]
# Generate a token for `Santa` using our calculated value for `n`
santa_token = generateToken('Santa Claus')
# Use the self-generated token to login as Santa
R.recvuntil(b'Enter option:')
R.sendline(b'2')
R.recvuntil(b'name:')
R.sendline(b'Santa Claus')
R.recvuntil(b'token:')
R.sendline(santa_token)
# Use option 4 to view the wishlist and get the flag
R.interactive()
Forensic
See You
We are given a PCAP file with the instructions that one the machines was found to be exfiltrating information. Wireshark’s protocol statistics show a bunch of TLS traffic (which we can ignore) and some UDP traffic. A large portion of the UDP traffic comes from port 38884.
% tshark -r artifact.pcapng -z io,phs
#<snip>
===================================================================
Protocol Hierarchy Statistics
Filter:
eth frames:21247 bytes:23866862
ip frames:21227 bytes:23865225
udp frames:18993 bytes:1295197
data frames:18351 bytes:1248704
dns frames:236 bytes:24597
mdns frames:8 bytes:712
llmnr frames:1 bytes:67
jmirror frames:23 bytes:1817
ipv6 frames:22 bytes:1748
_ws.malformed frames:19 bytes:1476
data frames:2 bytes:182
ip frames:1 bytes:69
_ws.malformed frames:1 bytes:69
ssdp frames:18 bytes:3766
dhcp frames:2 bytes:666
tcp frames:2231 bytes:22569848
tls frames:823 bytes:21959388
tcp.segments frames:527 bytes:20067651
tls frames:510 bytes:20007994
http frames:36 bytes:12865
data-text-lines frames:11 bytes:6776
igmp frames:3 bytes:180
ipv6 frames:12 bytes:1229
icmpv6 frames:3 bytes:270
udp frames:9 bytes:959
mdns frames:8 bytes:872
llmnr frames:1 bytes:87
arp frames:8 bytes:408
===================================================================
% tshark -r artifact.pcapng -Y 'udp.srcport == 38884' -T fields -e 'udp.dstport' | cut -c 3- | awk '{printf "%c",$0}' | xxd
00000000: 8950 4e47 0d0a 1a0a 0000 000d 4948 4452 .PNG........IHDR
00000010: 0000 0376 0000 0110 0802 0000 0073 fd71 ...v.........s.q
00000020: b400 0000 0173 5247 4200 aece 1ce9 0000 .....sRGB.......
# <snip>
% tshark -r artifact.pcapng -Y 'udp.srcport == 38884' -T fields -e 'udp.dstport' |
# ^^ Read the PCAP file, filter by udp source port == 38884, and extract only the UDP target port
cut -c 3- | # ignore the first 2 digits and capture the rest
awk '{printf "%02x",$0}' | # Convert from decimal to hex
xxd -r -p > cu.png # convert from hex string to byte values and store it as 'cu.png'
Open the resulting image file to read the flag.

References & Writeups
- https://www.alpertron.com.ar/ECM.HTM
- https://mechfrog88.github.io/wargames-2023
- https://zeynarz.github.io/posts/wgmy23/
- https://hackmd.io/@capri/BkeRmUo8T
- https://zachwong02.github.io/post/wgmy2023-compromised/
- https://vicevirus.github.io/posts/warmupweb-wgmy-2023/
- https://jerit3787.github.io/ctf/posts/wargamesmy-2023-writeup/
- https://zachwong02.github.io/post/wgmy2023-seeyou/
- https://d0ublew.github.io/categories/wgmy2023/
- https://github.com/jasonpeh373/Wargame2023-RE
- https://github.com/ItsZer01/CTF-Writeup/blob/main/2023/Wgmy2023.md
- https://mechfrog88.github.io/wargames-2023
- https://davidtan0527.github.io/ctfs/wargamesmy2023/magic_door
- https://github.com/4n86rakam1/writeup/tree/main/Wargames.MY_2023_CTF
Challenges
Category Challenge Description CRYPTO Hohoho 2 Continue CRYPTO Hohoho 2 CRYPTO N-less RSA FORENSIC Can’t Snoop FORENSIC Compromised FORENSIC SeeYou MISC Dialect MISC Sayur MISC Splice MISC Warmup - Game OTHER Feedback Form PPC Linux Memory Usage PPC Lokami Temple PWN Free Juice PWN Magic Door PWN Pak Mat Burger REVERSE Defeat the boss! REVERSE RmRf WEB My First AI Project WEB Pet Store Viewer WEB Report Google? WEB Secret WEB Status WEB Truco WEB Warmup - Web WEB myCloud
